Introduction to Aging and Reversal Possibilities
Understanding Aging: Biological Perspectives
Aging is an inevitable process characterized by the gradual decline of physiological functions over time. It not only affects the quality of life but also increases the risk for various age-related diseases. Biologically, aging is associated with changes at the cellular and molecular levels, including the shortening of telomeres, accumulation of oxidative damage, and increased presence of senescent cells.
Current Anti-Aging Interventions and Limitations
Current interventions to combat aging include lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatments, and emerging therapies like stem cell transplantation and senotherapeutics. However, these strategies have limitations. Invasive procedures carry risks, lifestyle changes may not provide definitive efficacy, and the full potential of senotherapeutics is not yet realized due to their complexity and the infancy of clinical applications.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: An Overview
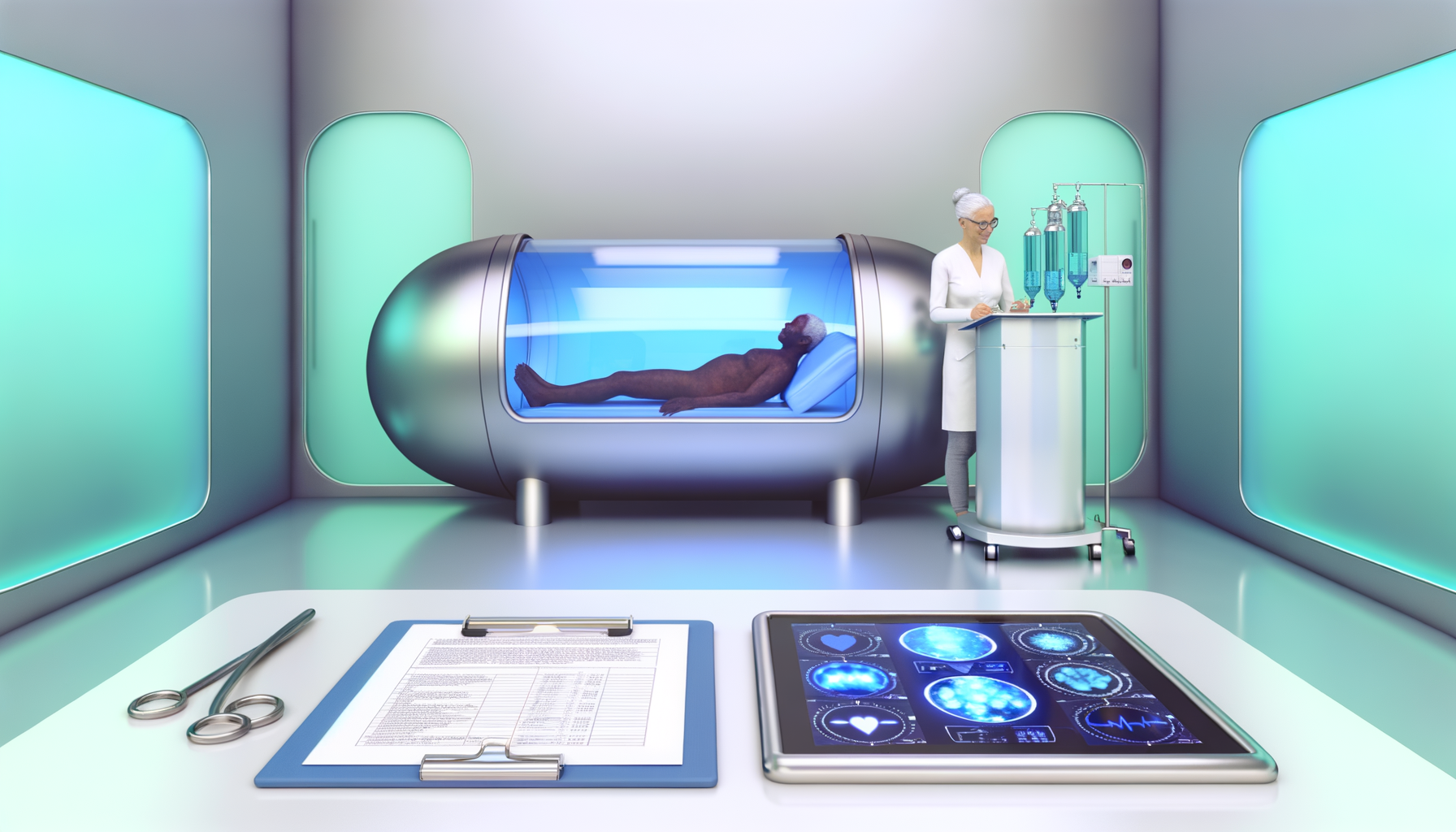
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a noninvasive treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment. Originally used for hypoxia-related conditions, HBOT has gained attention for its potential in addressing aging and age-related diseases. By increasing oxygen content in plasma, HBOT can induce various beneficial cellular and biochemical changes.
The Promise of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Reversing Aging
Recent studies suggest that HBOT may have the potential to reverse certain aspects of the aging process. By enhancing oxygen delivery to tissues, HBOT has been shown to promote angiogenesis, reduce inflammation, and possibly extend telomere length and reduce senescent cell accumulation. These findings offer a promising glimpse into the potential of HBOT as a therapy for healthy aging, warranting further research to fully understand its mechanisms and implications.

Feeling You Have a Right to Safe Beauty & Fem Care?
If so, it may be time for a change. It starts with knowledge. We have a few suggestions in our new guides.
The Science Behind Aging
Role of Telomeres in Aging
The aging process is intrinsically linked to the length and integrity of telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. Each time a cell divides, telomeres shorten, eventually leading to cellular senescence or apoptosis when they become critically short. This progressive shortening is a key biomarker of aging and is associated with an increased risk of age-related diseases. The enzyme telomerase can extend telomere length and potentially slow the aging process, but its activity is limited in most somatic cells.
Free Radicals and Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to detoxify their harmful effects through neutralization by antioxidants. Free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules with unpaired electrons, can cause significant damage to cell structures, including DNA, proteins, and lipids. This damage accumulates over time, contributing to the aging process and the development of various age-related conditions.
Senescent Cells and Their Impact on Aging
As cells age, they often enter a state of senescence, where they cease to divide but do not die. These senescent cells can accumulate in tissues, secreting pro-inflammatory factors that contribute to tissue dysfunction and the progression of age-related diseases. The removal or clearance of senescent cells is a promising therapeutic target to improve healthspan and potentially reverse aspects of aging.
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Aging
The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors such as lifestyle, diet, and exposure to toxins plays a crucial role in determining the rate and extent of aging. While genetic factors set a baseline for an individual’s aging trajectory, environmental influences can modulate gene expression and impact the biological aging process. Interventions that promote a healthy environment for cells, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of harmful exposures, can support healthier aging.

Do you have the most commonly used but toxic, disease bringing chemicals in your skin care? Many chemicals in skincare are hormone disruptors and make menopause symptoms worse.
Find out more…
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Explained
Mechanism of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. In a hyperbaric oxygen chamber, the air pressure is increased to up to three times higher than normal air pressure. Under these conditions, your lungs can gather more oxygen than would be possible breathing pure oxygen at normal air pressure. This high level of oxygen is then carried throughout the body in the bloodstream, where it helps fight bacteria and stimulate the release of substances called growth factors and stem cells, which promote healing.
Traditional Uses of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
HBOT has been traditionally used to treat a range of conditions, including decompression sickness (a hazard of scuba diving), serious infections, bubbles of air in your blood vessels, and wounds that may not heal as a result of diabetes or radiation injury. In these conditions, HBOT can be the primary treatment or part of a treatment plan. It works by restoring normal levels of blood gases and tissue function to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Decompression Sickness: Also known as “the bends,” this condition occurs in divers who surface too quickly. HBOT helps by reducing the volume of gas bubbles formed in the bloodstream.
- Infections: HBOT increases oxygen concentration in all body tissues and can help with fighting certain types of anaerobic bacterial infections.
- Air or Gas Embolism: HBOT can reduce the size of air bubbles that enter blood vessels.
- Non-Healing Wounds: For people with diabetes or radiation injuries, HBOT can encourage new blood vessels to grow and bring more oxygen to the wound site, which promotes healing.
The Process of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment
The process of HBOT involves several steps:
- Assessment: A medical professional will assess the patient’s condition to determine if HBOT is appropriate.
- Preparation: The patient may be asked to remove clothing and wear a hospital gown to ensure no sources of ignition are present in the oxygen-rich environment.
- Entering the Chamber: The patient enters the hyperbaric oxygen chamber, which can be a unit designed for one person (monoplace) or several people (multiplace).
- Pressurization: The chamber is sealed, and the internal pressure is gradually increased.
- Oxygen Delivery: The patient breathes pure oxygen through a mask or hood.
- Treatment Duration: Each session can last from 60 to 90 minutes, and the number of sessions can vary based on the medical condition being treated.
- Monitoring: Throughout the treatment, healthcare professionals monitor the patient and the chamber’s pressure.
- Completion: After the treatment, pressure is slowly returned to normal, and the patient exits the chamber.
It is important to note that while HBOT is generally safe, it can have side effects such as temporary nearsightedness, middle ear injuries, lung collapse, and seizures due to oxygen toxicity. These risks are typically managed by healthcare professionals who are trained in hyperbaric medicine.

Doubting chemicals in skincare and femcare? Well done! Choose chemical-free products whenever possible.
Recent Studies on Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Aging
The Israeli Study: Methodology and Participants
The Israeli study, a groundbreaking piece of research, explored the potential of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) in reversing the aging process. The methodology involved a controlled trial with participants aged 64 and older. These individuals underwent a series of 60 daily HBOT sessions, each lasting 90 minutes, with 100% oxygen at 2 ATA (atmospheres absolute) with five-minute air breaks every 20 minutes. The study’s primary aim was to observe changes in telomere length and the reduction of senescent cells, which are both considered key indicators of aging.
Findings: Telomere Lengthening and Senescent Cell Reduction
The findings of the study were significant, showing that post-HBOT, participants exhibited a considerable increase in telomere length of up to 20% in certain types of blood cells. Additionally, there was a marked reduction in the number of senescent cells, particularly in the T helper cells, by an average of 37%. These results suggest that HBOT can positively affect cellular aging and potentially reverse the aging process at a biological level.
Implications of the Study
The implications of this study are profound, suggesting that HBOT could be a viable non-pharmacological treatment for aging. By lengthening telomeres and reducing senescent cells, HBOT may not only slow down the aging process but may also improve the quality of life by reducing the risk of age-related diseases. This research opens new avenues for anti-aging therapies, emphasizing the importance of cellular health in the overall aging process.
Limitations and Areas for Further Research
Despite the promising results, the study has limitations that warrant further research. The sample size was relatively small, and the study only included participants who were in relatively good health for their age. Additionally, the long-term effects of HBOT on aging are not yet fully understood, and further studies are needed to determine the optimal frequency and duration of HBOT sessions for anti-aging benefits. Future research should also explore the mechanisms behind the observed effects, the potential impact on different age groups, and the efficacy of HBOT in conjunction with other anti-aging interventions.
By the way, something for you, a little gift!!!
I am just in the middle of publishing my book. It’s about How women can balance their hormones. One part is about food and diet, of course.
Follow this link and enter your email.
I will send you this part of the book for free once the book is published. It has many concrete, practical tips and recipes and will help you feel better during menopause or times of Big hormonal fluctuations.
Annette, Damiva Lead for Health & Wellness

Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact on Aging
Dietary Considerations and Anti-Aging Foods
The foods we consume play a critical role in the aging process. A diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can combat oxidative stress, a key contributor to cellular aging. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and walnuts, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, polyphenols found in berries and dark chocolate have been linked to increased longevity. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into one’s diet can help maintain cellular health and slow the aging process.
The Role of Fasting and Caloric Restriction
Fasting and caloric restriction have been shown to have potential anti-aging effects. Intermittent fasting, which cycles between periods of eating and fasting, can trigger cellular repair processes and improve metabolic health. Caloric restriction, reducing calorie intake without malnutrition, has been associated with longer lifespan in various animal studies. These practices may reduce the risk of age-related diseases and promote a longer, healthier life.
The Effects of Sleep, Exercise, and Social Engagement
Quality sleep is essential for the body’s repair mechanisms, and chronic sleep deprivation can accelerate aging. Regular exercise boosts cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles, and enhances cognitive function, acting as a powerful anti-aging tool. Social engagement and maintaining strong relationships contribute to emotional well-being and have been linked to longer lifespans. These lifestyle factors are integral to a holistic approach to healthy aging.
Harmful Habits and Their Influence on Aging
Habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can significantly accelerate the aging process. Smoking contributes to oxidative damage and inflammation, while excessive alcohol can lead to nutritional deficiencies and organ damage. Avoiding these harmful habits is crucial for preserving youthfulness and preventing premature aging.

Bette 100% All-Natural Relaxing Lavender Body Lotion.
Chemical-Free
Your relaxing night time body moisturizer to leave the day’s stress behind. Decompress and wish your body good night with the calming scent of lavender.
Complementary Anti-Aging Strategies
Natural Senolytics and Their Potential
As the quest for the fountain of youth continues, natural senolytics have emerged as a promising avenue in the anti-aging arena. Senolytics are agents that selectively induce death of senescent cells—cells that have stopped dividing and contribute to age-related tissue dysfunction. By clearing these cells, senolytics have the potential to improve tissue function and increase healthspan. Natural compounds such as quercetin, found in apples and onions, and fisetin, abundant in strawberries, have shown senolytic activity. These compounds, along with others like curcumin and resveratrol, are being investigated for their ability to mitigate the accumulation of senescent cells, thereby potentially slowing the aging process and reducing the risk of age-related diseases.
Supplements and Nutrients with Anti-Aging Properties
Supplementation with certain vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients can support the body’s anti-aging mechanisms. Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene combat oxidative stress, a key contributor to aging. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties and are linked to improved brain health. Coenzyme Q10, a nutrient that supports energy production in cells, has been associated with improved skin health and reduced signs of aging. Additionally, supplements like nicotinamide riboside and nicotinamide mononucleotide are being studied for their potential to boost levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme involved in numerous metabolic processes and associated with longevity.
The Interplay Between Lifestyle Modifications and Anti-Aging Therapies
Lifestyle choices play a critical role in the aging process, and when combined with anti-aging therapies like hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), they can synergistically enhance overall health and longevity. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support cellular health. Regular physical activity promotes cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and cognitive function. Adequate sleep is vital for tissue repair and cognitive health. Stress management techniques such as meditation and mindfulness can reduce the detrimental effects of chronic stress on the body. Avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption further protects the body from premature aging. When these lifestyle modifications are paired with targeted anti-aging therapies, individuals may experience a more profound anti-aging effect, leading to a better quality of life and potentially a longer lifespan.
Conclusion: The Future of Anti-Aging Research and Therapies
Summarizing the Potential of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) has emerged as a compelling candidate in the quest to mitigate the effects of aging. By delivering 100% oxygen at pressures exceeding atmospheric levels, HBOT has been traditionally utilized for conditions related to hypoxia. Its therapeutic scope, however, has expanded to include a range of disorders, leveraging its ability to induce various cellular, biochemical, and physiological changes. The potential of HBOT in the context of aging lies in its multifaceted impact on the body, including the promotion of angiogenesis, reduction of inflammation, enhancement of antioxidant defenses, interference with cellular senescence, and regulation of stem cell dynamics. These mechanisms collectively suggest that HBOT could play a significant role in promoting healthy aging and potentially reversing certain aging processes.
The Importance of Holistic Approaches to Aging
While HBOT presents a promising avenue for anti-aging interventions, it is crucial to recognize the importance of holistic approaches to aging. Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management play pivotal roles in influencing the aging process. Dietary patterns rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods, caloric restriction, and intermittent fasting have been associated with longevity. Similarly, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and social engagement contribute to a reduced risk of age-related diseases and improved quality of life. Therefore, integrating HBOT with these lifestyle modifications could potentially amplify its anti-aging effects, underscoring the need for a comprehensive strategy in addressing the complexities of aging.
Continued Research and Ethical Considerations
The therapeutic implications of HBOT in aging are supported by pre-clinical and small-scale clinical studies, but there is a pressing need for further research. Future studies should aim to elucidate the systemic effects of HBOT on the aging process, optimize treatment protocols, and establish its efficacy and safety in larger populations. Additionally, ethical considerations must be taken into account, particularly when it comes to accessibility and the potential for disparities in the availability of anti-aging therapies. As research progresses, it is imperative to ensure that advancements in anti-aging treatments, including HBOT, are guided by principles of equity and justice.