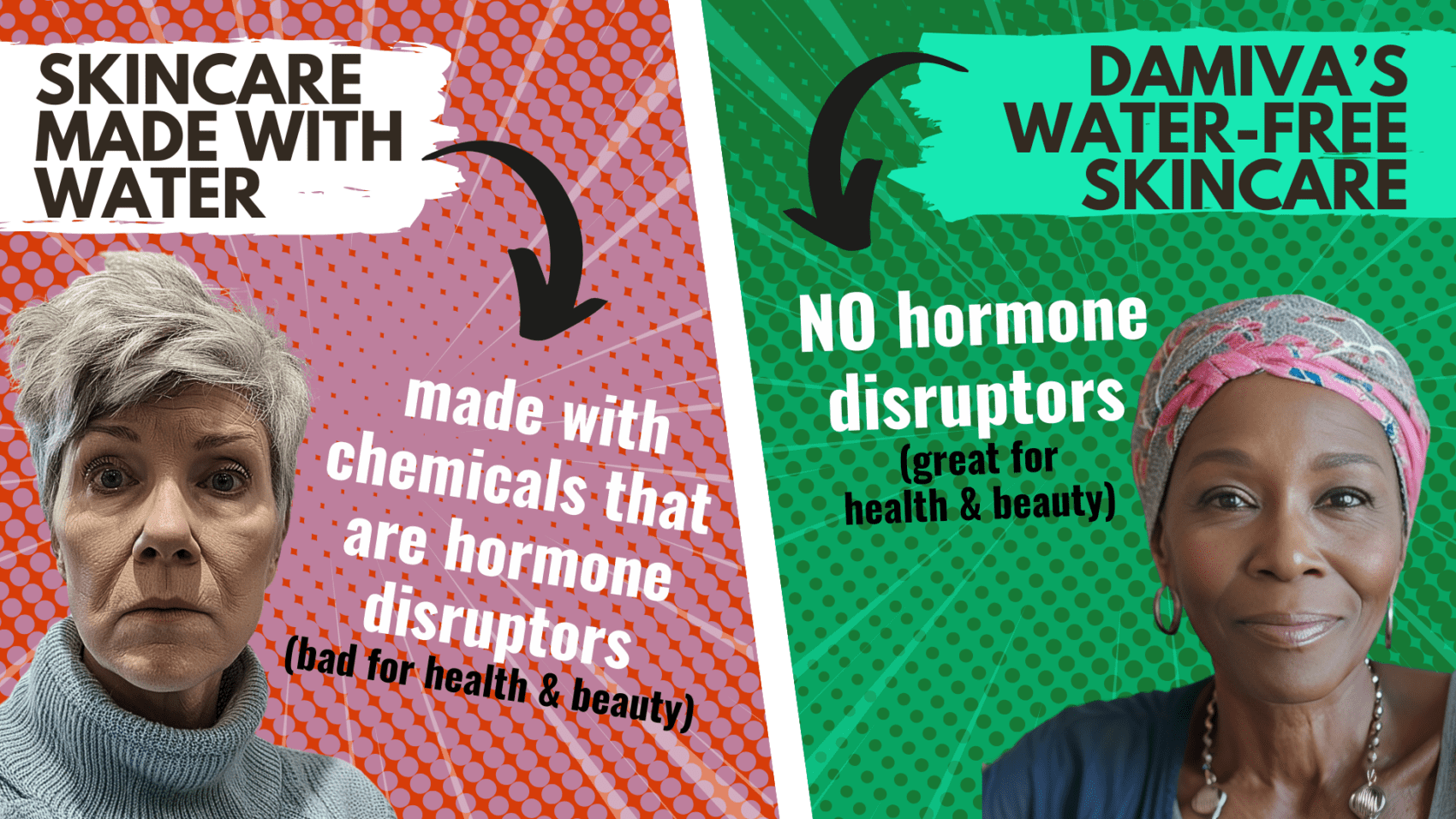
Introduction to Preservatives and Health
Overview of Chemical Preservatives
Chemical preservatives are substances added to products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In our daily lives, they are ubiquitous, found in foods, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and other household products. While they extend shelf life and maintain product integrity, there is growing concern about their potential health impacts, particularly when these chemicals come into contact with sensitive areas of the body, such as the vagina.

⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
“I needed a product like this for medical reasons. Thanks to this product I was able to do my physical therapy. The formula is very comfortable. It provides the right amount of lubrication. I will continue to use. I’m very happy to have found this because nothing else was working.”
Beatriz E, Cleo Customer
The Importance of the Cedars Sinai Study
A pivotal study conducted by researchers at Cedars Sinai Medical Center has shed light on the implications of preservative exposure on vaginal health. The study highlighted how certain chemicals, including those used as preservatives, can disrupt the delicate balance of the vaginal microbiome and epithelial integrity. This disruption can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, irritation, and other gynecological issues.
Ethical Considerations in Human Trials
When it comes to assessing the safety of chemical preservatives, ethical considerations in human trials are paramount. The potential risks associated with exposure to these chemicals necessitate stringent ethical guidelines to ensure participant safety and informed consent. The Cedars Sinai Study, among others, has navigated these ethical waters carefully, paving the way for a deeper understanding of preservative impacts under rigorous scientific scrutiny.
Prevalence of Chemical Preservatives in Daily Life
Chemical preservatives are nearly inescapable in modern life. From the parabens in personal care products to the sodium benzoate in our food supply, these chemicals are encountered with a frequency that may surprise the average consumer. Their prevalence raises important questions about cumulative exposure and the potential for chronic health effects, particularly in sensitive populations or in sensitive areas of the body like the vagina.

⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ “My biggest symptoms are GSM, and because of Mae, they are mostly addressed. I have lived Mae for almost 7 years, and I endorse it all the time.” Margaret C., Damiva Mae Customer
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ “I’m in my 60’s and post menopause. My doctor recommended I try Damiva MAE, after taking me off hormones (due to developing cysts). I LOVE it. All natural, no hormones, Great vaginal moisturizer. Easy to insert and pleasant smell. So Thankful for MAE.” Paula, Damiva Mae Customer
Effects of Preservatives on Hormonal Function
Disruption of Hormone Production
Chemical preservatives, particularly parabens, have been implicated in the disruption of hormone production. Parabens, which are widely used as preservatives in cosmetics, personal care products, and even foods, can mimic estrogen, a primary female sex hormone, and interfere with the endocrine system. This mimicry can lead to an imbalance in hormone levels, as the body may respond to these chemicals as if they were naturally occurring estrogens. The disruption of hormone production is particularly concerning because hormones regulate a myriad of bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproductive health.
Consequences of Hormonal Imbalance
The consequences of hormonal imbalance due to exposure to chemical preservatives can be far-reaching. In women, an excess of estrogen-like substances can lead to menstrual irregularities, early onset of puberty, and increased risk of hormone-related cancers such as breast cancer. In men, exposure to estrogenic chemicals can result in decreased sperm count, testicular atrophy, and infertility. Hormonal imbalances can also affect the thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism, and can contribute to weight gain, fatigue, and other metabolic disorders.

Do you have the most commonly used but toxic, disease bringing chemicals in your skin care? Many chemicals in skincare are hormone disruptors and make menopause symptoms worse.
Find out more…
Specific Health Issues Related to Preservatives
- Reproductive Health: Studies have shown that parabens can adversely affect the quality of sperm and may lead to reduced fertility in males. In females, these chemicals have been associated with reproductive disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis.
- Developmental Concerns: Prenatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting preservatives can lead to developmental and reproductive issues in offspring, including altered development of reproductive organs and potential long-term fertility problems.
- Obesity and Metabolic Disorders: Hormonal disruption can also contribute to the development of obesity and related metabolic disorders. Chemical preservatives can interfere with the hormones that regulate appetite, fat storage, and insulin sensitivity, potentially leading to conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
Given the potential for these health issues, it is critical to understand the sources of exposure to harmful preservatives and to take steps to minimize contact with these chemicals.
Preservatives and Vaginal Health
Impact on Vaginal Dryness and Discomfort
The vaginal ecosystem is delicate and highly responsive to hormonal changes. Preservatives such as parabens and triclosan, commonly found in personal care products, have been shown to disrupt hormone function. This disruption can lead to a decrease in estrogen levels, which is critical for maintaining vaginal lubrication and elasticity. The result is an increased risk of vaginal dryness and discomfort, conditions that not only cause irritation but can also affect the overall quality of life and sexual health of women.
Association with Painful Intercourse
When vaginal dryness occurs, it often leads to dyspareunia, or painful intercourse. This condition can create a negative cycle of pain and anxiety around sexual activity, leading to decreased libido and strained intimate relationships. The presence of chemical preservatives in personal lubricants and other intimate products can exacerbate this issue, as some of these substances can cause irritation or damage to the vaginal and vulvar tissues, further contributing to painful experiences during intercourse.
Link to Bacterial Vaginosis and Immune System
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection that occurs when the balance of bacteria in the vagina is disrupted. Studies have suggested a link between the use of products containing chemical preservatives and an increased risk of developing BV. This condition not only causes discomfort and discharge but can also lead to more serious reproductive health issues if left untreated. Moreover, the presence of these chemicals can weaken the immune system’s response in the vaginal area, making it more susceptible to infections and reducing its ability to maintain a healthy balance of flora.
In conclusion, the use of preservatives in products that come into contact with the vaginal area can have significant negative impacts on vaginal health. These include hormonal disruptions leading to dryness and discomfort, an association with painful intercourse, and a potential increase in the risk of infections like bacterial vaginosis. It is essential for women to be aware of these risks and consider the ingredients in their personal care products carefully.
Preservatives in Pregnancy and Fetal Health
Risks of Chemical Exposure During Pregnancy
Exposure to chemical preservatives during pregnancy poses significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Chemical preservatives, such as parabens, have been linked to a range of adverse health outcomes due to their ability to mimic estrogen and disrupt endocrine function. The delicate hormonal balance necessary for normal fetal development can be altered by these chemicals, potentially leading to developmental and reproductive issues. The Cedars Sinai Study has highlighted the importance of understanding the effects of preservatives on human tissues, as animal studies may not fully capture the nuances of human biology.
During pregnancy, the placenta acts as a barrier to protect the developing fetus; however, it is not impervious to all chemicals. Preservatives found in everyday products can cross this barrier, leading to potential exposure of the fetus to toxic substances. This exposure is particularly concerning during critical periods of development when organ systems are forming and the fetus is most vulnerable to environmental insults.

Feeling You Have a Right to Safe Beauty & Fem Care?
If so, it may be time for a change. It starts with knowledge. We have a few suggestions in our new guides.
Fetal Disorders Linked to Preservatives
Research has indicated a correlation between prenatal exposure to chemical preservatives and the occurrence of fetal disorders. For instance, studies have shown that exposure to parabens can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction in the testes of the F1 generation, as demonstrated by a decrease in the respiratory control index and inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase activity. This mitochondrial disruption can have far-reaching consequences on male fertility, including reduced sperm count and compromised sperm quality.
Furthermore, the presence of parabens during gestation has been associated with alterations in the antioxidant capacity of several organs in the F1 generation. This imbalance in oxidative stress parameters may predispose the offspring to a variety of health issues later in life, including metabolic disorders and increased susceptibility to oxidative damage.
It is also worth noting that the use of parabens during pregnancy has been linked to changes in the expression of certain cytokines, which are crucial for proper neurodevelopment. Disruptions in the cytokine network can have implications for the neurological health of the offspring, potentially leading to behavioral and cognitive deficits.

Doubting chemicals in skincare and femcare? Well done! Choose chemical-free products whenever possible.
In summary, the evidence suggests that the use of chemical preservatives during pregnancy can lead to significant changes in both the mitochondrial bioenergetics and the antioxidant capacity of the offspring’s organs, with potential long-term health implications. As such, it is imperative to consider the risks associated with exposure to these chemicals during pregnancy and to take steps towards reducing or eliminating their use in products that may come into contact with pregnant women.
Environmental and Lifestyle Exposure to Preservatives
Sources of Chemical Preservatives in the Environment
Chemical preservatives are ubiquitous in the environment, stemming from a variety of sources. Industrial processes, agricultural practices, and consumer products all contribute to the widespread distribution of these compounds. Industrial solvents, lubricants, and their byproducts, such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dioxins, are persistent environmental pollutants that can leach into soil and groundwater. Pesticides and fungicides used in agriculture can also leave residues that enter the food chain and water systems. Additionally, pharmaceutical agents like diethylstilbestrol (DES) have been detected in the environment, posing potential risks for endocrine disruption.
Daily Products and Their Preservative Content
Everyday products, from personal care items to household cleaners, often contain chemical preservatives to extend shelf life and prevent microbial growth. Common preservatives such as parabens, phthalates, and formaldehyde-releasing agents are found in items like shampoos, lotions, and cosmetics. Food products are not exempt, with preservatives like BHA, BHT, and sulfites being added to processed foods to maintain freshness. The widespread use of these chemicals means that daily exposure is almost inevitable for most individuals.
The Role of Plastic in Chemical Exposure
Plastics play a significant role in chemical exposure due to their pervasive use and the presence of substances like bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, which can leach out over time. These chemicals are known to act as endocrine disruptors, interfering with hormonal function. Plastic containers used for food and beverage storage are of particular concern, as heat and wear can increase the rate of leaching. The prevalence of plastic in packaging, toys, and even medical devices makes it a critical vector for chemical preservative exposure.
In conclusion, the presence of chemical preservatives in the environment and daily products is a significant concern due to their potential impact on hormonal function and overall health. Understanding the sources and pathways of exposure is essential for mitigating risks and protecting vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women and developing fetuses, from the adverse effects of these chemicals.
Reducing Exposure to Harmful Preservatives
Alternatives to Plastic Products
With the growing concern over the health implications of chemical preservatives found in plastics, it is essential to consider alternative materials that are safer for both personal use and the environment. Stainless steel, glass, and ceramic are excellent options for replacing plastic containers and bottles. These materials do not leach chemicals and are often more durable and sustainable. For instance, stainless steel water bottles can serve as a lifelong investment, replacing countless single-use plastic bottles. Similarly, glass or ceramic containers for food storage are not only safer but also help in maintaining the flavor and freshness of the food.
Safe Storage and Preparation of Food
Proper food storage and preparation play a crucial role in minimizing exposure to harmful preservatives. It is advisable to store food in glass or stainless steel containers rather than plastic ones, especially when reheating in a microwave. Additionally, using non-plastic utensils for cooking can reduce the risk of chemical leaching at high temperatures. When purchasing food, opt for fresh or frozen produce over canned goods, as cans are often lined with preservative-laden materials.
Identifying and Avoiding High-Risk Plastics
Understanding the recycling codes on plastic products can help in identifying high-risk plastics that contain harmful preservatives. Plastics labeled with recycling symbol #3, which indicates the presence of PVC (polyvinyl chloride), should be avoided due to their high chemical content. It is also crucial to avoid heating food in plastic containers, as heat can accelerate the leaching process. By being vigilant and informed about the types of plastics used in everyday products, individuals can make safer choices for their health and the environment.
In conclusion, reducing exposure to harmful preservatives is achievable through conscious choices in the products we use daily. By opting for safer materials, practicing safe food storage and preparation, and being informed about the risks associated with certain plastics, we can take significant steps towards a healthier lifestyle and a reduced chemical burden on our bodies.
Do you know the 3 main ways how your body is exposed to harmful chemicals, which affect your hormones, your thyroid, health and beauty?
If not, it may be time to learn about them. It takes about 1-2 minutes.
We have a few suggestions how to avoid these silent health and immune system killers in our new guide.

Conclusion: Steps Towards a Healthier Lifestyle
Summarizing the Impact of Preservatives
Throughout this article, we have explored the pervasive presence of chemical preservatives in our daily lives and their detrimental effects on hormonal function, vaginal health, pregnancy, and the environment. These substances, designed to extend the shelf life of products, can disrupt delicate hormonal balances and compromise the immune system. Their impact on the vagina is particularly concerning, as they can contribute to conditions like dryness, painful intercourse, and bacterial vaginosis. Moreover, the exposure to preservatives during pregnancy raises the risk of fetal disorders, highlighting the need for vigilance and proactive measures to reduce chemical exposure.
Positive Health Impacts of Reducing Chemical Burden
Reducing the chemical burden on our bodies can lead to significant health benefits. By choosing products free from harmful preservatives, we can support our hormonal health and reduce the risk of associated health issues. Embracing a lifestyle that minimizes exposure to these chemicals can also enhance vaginal health, leading to a decrease in discomfort and infections. Furthermore, for expecting mothers, limiting exposure to preservatives can contribute to healthier fetal development. The environment also benefits from reduced chemical usage, as it lessens the ecological footprint and supports biodiversity.
Encouragement for Incremental Changes
Transitioning to a healthier lifestyle doesn’t require drastic changes overnight. Small, incremental steps can make a significant difference in reducing exposure to harmful preservatives. Start by identifying high-risk plastics and preservative-laden products in your daily routine and seek out safer alternatives. Gradually shift towards storing and preparing food in ways that minimize chemical leaching. By making these changes progressively, we can collectively move towards a lifestyle that prioritizes health and well-being, while also being mindful of the environment.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of preservatives on our health and environment is the first step towards making informed choices. By taking incremental steps to reduce our chemical exposure, we can enjoy the positive health impacts and contribute to a healthier, more sustainable world.