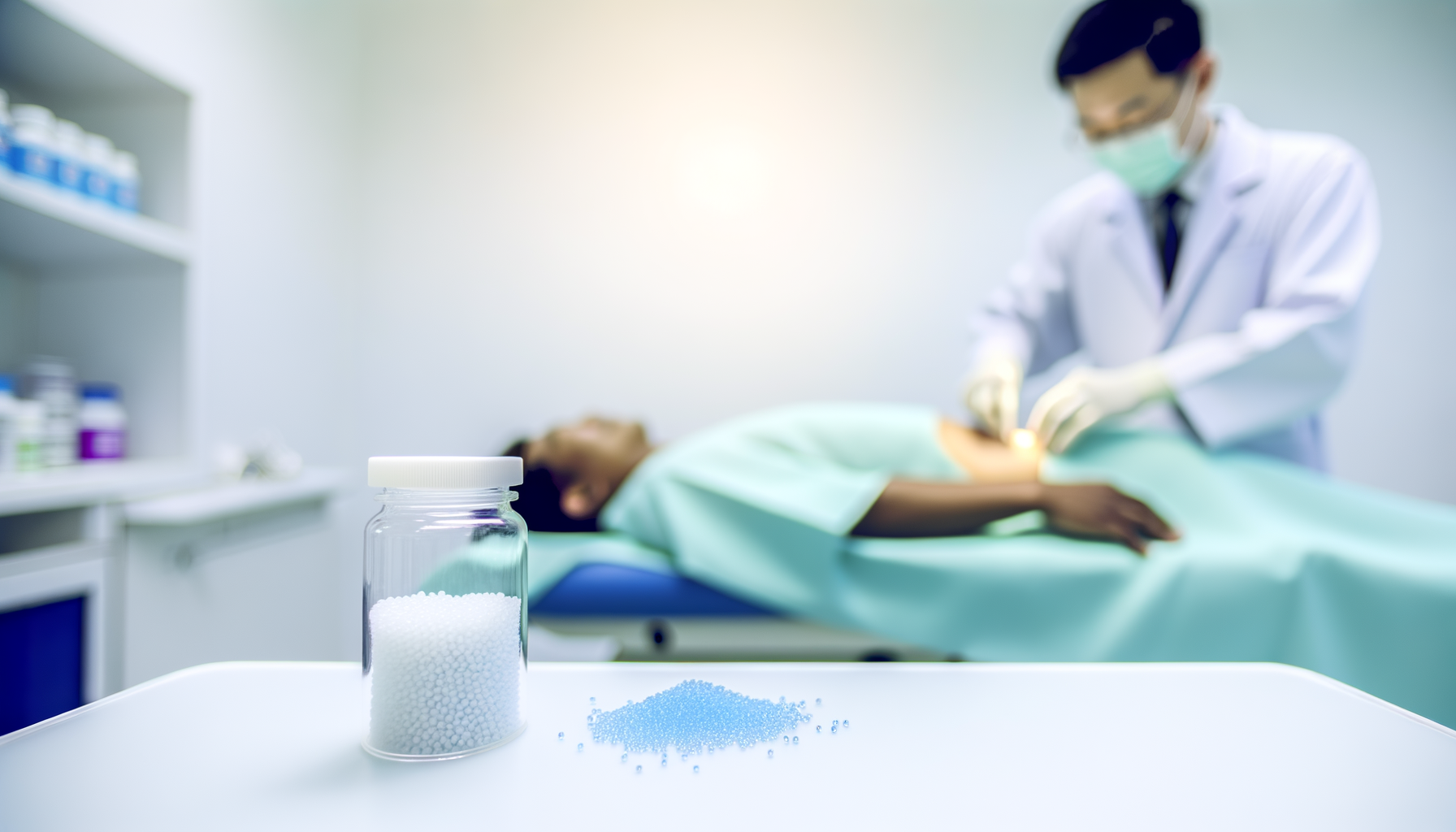
Introduction to Hormone Pellet Therapy
Hormone pellet therapy is a form of bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) that involves the subcutaneous insertion of a pellet—typically the size of a grain of rice—that slowly releases hormones into the body. These hormones are designed to mimic the body’s natural hormones, with the goal of restoring balance and alleviating symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances or declines due to aging.
Types of Hormones Used
The hormones commonly used in pellet therapy include estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. These bioidentical hormones are derived from plant sources and are molecularly identical to the hormones produced by the human body. They can be customized in dosage and combination to meet the specific needs of each individual patient.
General Uses in Different Populations
Hormone pellet therapy is utilized across various populations, primarily for individuals experiencing perimenopause, menopause, or andropause (the male equivalent of menopause). Symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, loss of libido, fatigue, weight gain, mood changes, and memory loss can be addressed through this therapy. While both men and women can benefit from hormone pellet therapy, the specific hormones and dosages are tailored to the unique requirements of each gender.
Overview of Procedure
The procedure for hormone pellet insertion is relatively straightforward and minimally invasive. It typically involves the following steps:
- A healthcare provider numbs a small area of skin, usually in the upper buttocks.
- A tiny incision is made, and the hormone pellet is inserted subcutaneously.
- The incision is then closed with steri-strips or a small bandage; no sutures are necessary.
- The pellet gradually dissolves over a period of three to six months, releasing a steady stream of hormones into the bloodstream.
This method of delivery is advantageous because it provides a consistent supply of hormones, avoiding the fluctuations that can occur with other forms of hormone therapy such as pills, patches, or injections. Additionally, the convenience of having a long-lasting treatment with only a few applications per year makes it an attractive option for those with busy lifestyles.
Bioidentical Hormones and Compounded Pellets
Source and Nature of Bioidentical Hormones
Bioidentical hormones are derived from plant estrogens that are chemically identical to those the human body produces. Estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone are among the most commonly used bioidentical hormones. These hormones are processed in a laboratory to precisely match the molecular structure of human hormones. The goal of bioidentical hormone therapy (BHRT) is to provide relief from the symptoms associated with hormonal imbalance, such as those experienced during menopause or andropause.
Compounding Process and Customization
Compounded bioidentical hormones are custom-made by pharmacists following a healthcare provider’s prescription. This customization allows for individualized hormone combinations tailored to a patient’s specific needs, which can be based on hormone levels measured through blood or saliva testing. Compounded hormones can be provided in various forms, including pellets, creams, patches, and gels. The pellets, which are about the size of a grain of rice, are inserted subcutaneously and release hormones consistently over time.
FDA Stance and Regulatory Concerns
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved certain bioidentical hormones, but it does not regulate compounded bioidentical hormones. This lack of regulation raises concerns about the purity, potency, and safety of compounded hormones. The FDA’s inability to approve these individualized mixtures is due to the impracticality of testing the myriad of potential combinations for efficacy and safety. As a result, compounded bioidentical hormones may carry risks due to variability in strength and purity.
Claims of Safety and Effectiveness
Proponents of compounded bioidentical hormone pellet therapy claim that it offers a safer and more effective alternative to conventional hormone therapy, with benefits such as consistent hormone levels and fewer side effects. However, these claims are not universally supported by scientific evidence. While some studies suggest benefits, the lack of randomized controlled trials and FDA approval means that the safety and effectiveness of compounded bioidentical hormones remain uncertain. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends FDA-approved hormone therapies over compounded ones due to these concerns.

Popular Read
Procedure of Hormone Pellet Insertion
Pre-procedure Considerations
Before undergoing hormone pellet therapy, several factors must be taken into account to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. A healthcare professional will evaluate a patient’s hormone levels, body mass index (BMI), and overall health to determine the appropriate hormone dosage. It is crucial to disclose any medical history, current medications, and allergies to the healthcare provider. Additionally, patients may be advised to undergo a salivary test to check hormone levels, although the accuracy of such tests is debated by organizations like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Step-by-Step Insertion Process
- Local Anesthesia: The area of insertion, typically the hip, is numbed using a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
- Incision: A small incision is made in the numbed area.
- Insertion: One or more hormone pellets, each about the size of a grain of rice, are inserted beneath the skin into the fatty tissue.
- Closure: The incision is closed with Steri-Strips or a stitch, and no sutures are typically required.
The procedure is relatively quick and is performed in an outpatient setting.
Post-procedure Care and Instructions
After the insertion of hormone pellets, patients must follow specific care instructions to ensure proper healing and absorption of the hormones. Activities involving the insertion site, such as swimming or intense exercise, should be avoided for a period, typically 4-7 days, to prevent complications like infection or pellet extrusion. The Steri-Strips or stitches used to close the incision are usually removed or dissolve on their own within 5-7 days. Patients should monitor the site for signs of infection and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Duration and Consistency of Hormone Delivery
Hormone pellets provide a steady, consistent release of hormones, mimicking the body’s natural hormone levels. This method avoids the peaks and troughs associated with other forms of hormone delivery, such as oral or transdermal applications. The pellets typically dissolve completely over a period of 3-6 months, depending on individual metabolism rates and activity levels. This method of delivery is designed to provide a more natural experience, with patients often reporting improvements in symptoms and overall well-being within a few days to weeks after the procedure.

Potential Benefits of Hormone Pellet Therapy
Symptom Relief and Quality of Life Improvements
Hormone pellet therapy has been associated with a range of benefits, particularly in terms of symptom relief and enhancing quality of life. For women, especially those going through menopause, hormone pellet therapy can alleviate hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings. Men may experience improvements in energy levels, mood, libido, and muscle mass. The steady release of hormones from the pellets can help stabilize these symptoms, providing a more consistent feeling of well-being compared to the fluctuations that can occur with other forms of hormone delivery.
Advantages Over Other Hormone Delivery Systems
One of the key advantages of hormone pellet therapy is the method of delivery. Unlike creams, patches, or oral medications that can create peaks and troughs in hormone levels, pellets provide a continuous, slow release of hormones directly into the bloodstream. This mimics the body’s natural hormone release more closely and avoids the first-pass metabolism by the liver, potentially reducing side effects and improving efficacy. Additionally, the convenience of not having to remember daily applications or pills is a significant benefit for many patients.
Anecdotal Evidence and Personalized Treatment
While scientific evidence is still evolving, anecdotal reports from patients and some healthcare providers suggest that hormone pellet therapy can lead to personalized treatment outcomes. Because the pellets are compounded for the individual and can be adjusted based on a person’s unique needs, some patients report better symptom control with pellet therapy compared to standardized hormone replacement therapies.
Comparison with FDA-approved Hormone Therapies
It’s important to note that while bioidentical hormone pellet therapy is not FDA-approved, some bioidentical hormones used in the pellets are FDA-approved in other forms. Patients and healthcare providers often weigh the benefits of pellet therapy, such as the convenience and steady hormone levels, against the more widely studied and regulated FDA-approved hormone therapies. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends FDA-approved hormone therapy as the standard of care, but some patients and providers report satisfaction with the results of pellet therapy despite the lack of FDA approval for this specific delivery method.
In conclusion, hormone pellet therapy may offer a range of potential benefits, including improved symptom relief, a more natural hormone delivery system, and the possibility of personalized treatment. However, it is essential for patients to discuss the risks and benefits with their healthcare provider, considering both anecdotal evidence and the current FDA stance on compounded bioidentical hormones.

Do you have the most commonly used but toxic, disease bringing chemicals in your skin care? Many chemicals in skincare are hormone disruptors and make menopause symptoms worse.
Find out more…
Safety and Side Effects
Common Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Hormone pellet therapy, like any medical treatment, comes with potential side effects and adverse reactions. The side effects experienced can vary depending on the individual’s response to the hormones, the levels, and types of hormones used. Common side effects in females receiving high doses of testosterone may include:
- Increased facial hair
- Acne
- Scalp hair loss
- Changes in menstrual cycle
- Deepening of the voice
For estradiol pellets, potential adverse effects listed on drug labels include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Period-like pains
- Yeast infections
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight changes
- Changes in libido
Long-term Risks and Hormone Level Monitoring
Long-term risks associated with hormone pellet therapy are not well-documented due to the lack of extensive research, particularly for compounded bioidentical hormones. Monitoring hormone levels is crucial to minimize risks, but the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) notes that salivary testing, often used by providers of compounded hormones, does not offer an accurate or precise method of hormone testing. Blood tests remain the standard for assessing hormone levels and adjusting treatment.
Contrast with Other Forms of Hormone Therapy
Compared to other forms of hormone therapy, hormone pellet therapy offers a unique delivery system that provides a steady release of hormones. However, the lack of FDA regulation for compounded hormones raises concerns about their purity and safety. Unlike FDA-approved hormone therapies, the strength and consistency of compounded hormones can vary, potentially leading to unpredictable therapeutic outcomes.
ACOG Recommendations and Guidelines
The ACOG recommends FDA-approved hormone therapies over compounded bioidentical hormones due to the regulatory oversight ensuring their safety, efficacy, and consistency. FDA-approved therapies have undergone rigorous testing and are accompanied by established guidelines for their use. Patients considering hormone pellet therapy should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider and consider ACOG’s recommendations when making treatment decisions.

Doubting chemicals in skincare and femcare? Well done! Choose chemical-free products whenever possible.
Cost and Accessibility
Average Costs and Factors Influencing Price
The cost of hormone pellet therapy can vary widely based on several factors. On average, patients might expect to pay close to $1,536 annually for the therapy. However, this figure can fluctuate depending on the provider, geographic location, and the specific hormones used. The dosage, determined by individual hormone levels and body mass index (BMI), also plays a significant role in the overall cost. Additionally, the frequency of pellet insertions, which typically occurs every 3-4 months, can affect the annual expense. It’s important to note that while some clinics offer in-house lab testing, others may require external lab services, adding to the cost.
Insurance Coverage and FDA Approval
Insurance coverage for hormone pellet therapy is not straightforward. FDA-approved hormone therapies are more likely to be covered by healthcare insurance, but the extent of coverage can vary among plans. Compounded bioidentical hormone therapy, which includes hormone pellet therapy, often lacks FDA approval due to concerns about the safety and effectiveness of these individually mixed hormones. As a result, most insurance companies are unlikely to cover compounded bioidentical hormone therapy. Patients considering this therapy should consult with their insurance providers to understand their coverage options and potential out-of-pocket costs.
Accessibility for Different Demographics
Hormone pellet therapy is accessible to various demographics, including menopausal women, transgender individuals, and others experiencing hormone imbalances. However, the accessibility of this treatment can be limited by factors such as cost, insurance coverage, and the availability of specialized providers. Since compounded bioidentical hormones are not FDA-approved, patients may face challenges in finding healthcare professionals who offer this service. Additionally, the lack of insurance coverage can make this therapy cost-prohibitive for some, potentially leading to disparities in access based on socioeconomic status. It is crucial for patients to thoroughly research providers and consider the long-term financial commitment before starting hormone pellet therapy.
Conclusion and Current Consensus
Summary of Hormone Pellet Therapy
Hormone pellet therapy is a form of hormone replacement therapy that involves the subcutaneous insertion of small, rice-sized pellets that release hormones steadily over time. This method utilizes bioidentical hormones, which are chemically identical to those naturally produced by the human body. The hormones commonly used in pellet therapy include testosterone, estradiol, and progesterone, and they are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances or deficiencies, such as those experienced during menopause or andropause.
Current Evidence and Expert Recommendations
The current body of evidence, including randomized controlled trials and observational studies, suggests that hormone pellet therapy can offer symptom relief and quality of life improvements for certain populations. For instance, postmenopausal women and men with testosterone deficiency have reported benefits in sexual health, bone mineral density, and overall well-being. However, the evidence also indicates potential risks, such as increased incidence of certain adverse events like gallbladder disease, venous thromboembolism, and in some cases, breast cancer.
Expert recommendations emphasize the importance of individualized treatment plans and careful monitoring of hormone levels to mitigate risks. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and other professional societies provide guidelines that generally support the short-term use of hormone therapy for symptom management, while being cautious about long-term use due to the potential for increased risks.
Final Thoughts on Patient Considerations
When considering hormone pellet therapy, patients and healthcare providers must engage in a thorough discussion about the potential benefits and risks. Factors such as the patient’s age, health history, personal preferences, and the severity of symptoms should be taken into account. It is also crucial for patients to understand the importance of adherence to post-procedure care and the need for regular follow-up appointments to monitor hormone levels and adjust dosages as necessary.
Cost and accessibility are additional considerations, as hormone pellet therapy may not be covered by all insurance plans, and the out-of-pocket expenses can be significant. Ultimately, the decision to pursue hormone pellet therapy should be made collaboratively, with a clear understanding of the current evidence and expert recommendations, as well as the patient’s individual health goals and concerns.